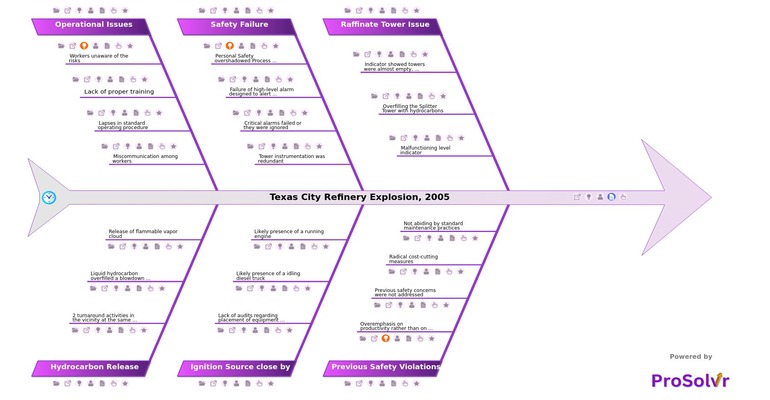
Root Cause Analysis of Texas City Refinery Explosion
The Texas City refinery explosion on March 23, 2005, inside the BP-owned refinery in Texas City was catastrophic, resulting in over 15 fatalities and more than 170 injuries. Conducting a thorough root cause analysis (RCA) based on Six Sigma principles can help prevent such disasters in the future. The blast heavily damaged or destroyed several refinery units, including the isomerization unit where the explosion originated. It also caused extensive damage to the surrounding community.
The force of the explosion was extremely powerful, causing extensive structural damage to the surrounding equipment and buildings within the refinery. Fires resulting from the explosion burned for several hours, worsening the damage. Secondary explosions further damaged the refinery infrastructure.
The refinery experienced significant operational disruptions, with repairs and lost production leading to substantial financial losses. BP reported losses of hundreds of millions of dollars due to the explosion. Additionally, the explosion released a significant amount of pollutants into the air, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other hazardous substances.
This raised concerns about air quality and potential long-term environmental health effects. Hydrocarbons, which are organic compounds consisting primarily of hydrogen and carbon atoms, can have various side effects on human health and the environment depending on their type, concentration, and exposure duration. Inhalation of hydrocarbon vapors can lead to respiratory problems such as coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and irritation of the throat and lungs. Some hydrocarbons, particularly polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and benzene, are known carcinogens. Chronic exposure increases the risk of developing cancers such as leukemia and lung cancer.
The Texas City Refinery Explosion is a stark reminder of the importance of root cause analysis and the need for continuous improvement in safety standards. By learning from past incidents and implementing robust corrective and preventive actions (CAPA), industries can enhance their quality and reliability. CAPA helps in identifying the root causes of problems, developing solutions, and preventing recurrence. This process ensures operational excellence, safer operations, and the protection of human lives and the environment. Tools like ProSolvr can play a pivotal role in executing CAPA effectively, ensuring that lessons learned lead to tangible improvements in safety and operational practices.
Understanding the lessons from the explosion is crucial. The tragedy underscores the need for stringent industrial safety standards in refineries of such scale and magnitude.
Who Can Learn from the Texas City Refinery Explosion?
The lessons from the Texas City Refinery Explosion, 2005, are relevant to a wide range of stakeholders. Industries related to oil and gas and chemical engineering can learn from the tragedy. Additionally, regulatory bodies and government agencies can use AI-powered root cause analysis to address such issues effectively and efficiently. Professionals working with occupational safety and health hazards can utilize GenAI-powered root cause analysis to analyze these problems. Emergency services and first responders, engineering and design professionals, and most importantly, corporate leadership and management teams can learn from this tragedy and work on corrective and preventive actions.
Why Use This Template?
Using the RCA Fishbone Diagram for the Texas City Refinery Explosion, 2005, can help identify the root causes such as safety failures, operational issues, the impact of radical cost-cutting measures, and ignoring previous safety threats. This visual root cause analysis enables teams to pinpoint critical issues and take corrective and preventive actions to ensure that management focuses more on safety and equipment upgrades rather than solely on productivity and profit. This approach enhances quality and reliability, leading to operational excellence and improved team efficiency.
Design and extend your template or reuse this with some modification for cause analysis of other problems in ProSolvr by smartQED. ProSolvr offers a platform to facilitate such detailed analyses, leveraging advanced tools to enhance problem-solving and decision-making processes.