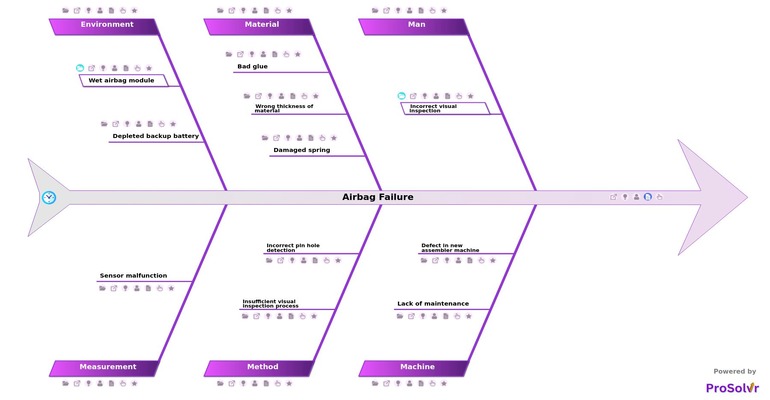
Reasons why an airbag fails to deploy and causes injury
In analyzing the recurring issues with airbags, various contributing factors need to be considered to address the root cause of the problem and ensure passenger safety. Defining the problem requires a comprehensive understanding of the symptoms, such as random deployment and failure during crashes, which necessitates causal factor analysis. Utilizing root cause analysis methods like fault tree analysis and failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), can help in identifying the real root of the problem, whether it lies in manufacturing defects, design flaws, or operational errors within the business process.
Implementing root cause analysis tools such as ProSolvr, Six Sigma tool for quality and reliability can assist in mapping out potential causes, including issues with airbag deployment mechanisms, sensor malfunctions, or inadequate quality control measures during production. Root cause analysis can uncover obstacles hindering effective airbag functionality and deployment in critical moments. To address the root cause effectively, it is imperative to perform a thorough investigation into the failures and deficiencies of the airbag system.
Recognizing that faulty airbags pose significant risks to occupants, it is essential to address the root cause of these failures through a structured problem-solving process. This involves not only addressing the symptoms of the problem but also delving deeper into the underlying factors contributing to airbag malfunctions. By addressing the root cause, manufacturers can improve the reliability and safety of airbag systems, thereby minimizing the occurrence of injuries and ensuring a safer journey for all vehicle occupants.
By conducting a comprehensive root cause analysis using the ProSolvr fishbone diagram, we can uncover the underlying issues contributing to airbag failures and take proactive measures to ensure the safety and well-being of vehicle occupants.
Who should use the Airbag Failure template?
Why use this template?