Root Cause Analysis of Corrosion Induced Leak
In 2015, Haldia Petrochemicals Limited (HPL) experienced a significant incident involving a corrosion-induced leak in its naphtha cracker unit. This leak was caused by corrosion in a high-temperature furnace, leading to the escape of hydrocarbons. The event underscored the critical issue of material degradation in petrochemical plants, where high-temperature environments and aggressive chemicals can accelerate corrosion.
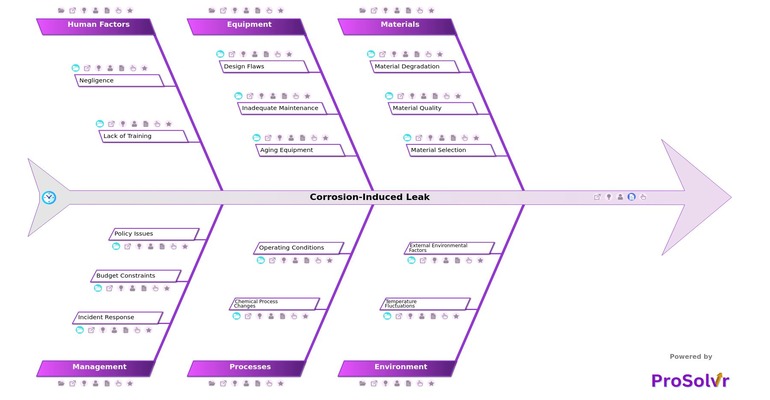
The leak raised concerns about maintenance practices and the integrity of the equipment, prompting a review of safety protocols and the implementation of more stringent inspection and monitoring systems to prevent future occurrences. This incident highlighted the importance of proactive measures to address corrosion to avoid operational disruptions and ensure plant safety. Conducting a root cause analysis (RCA) with a fishbone diagram (Ishikawa diagram) is crucial for addressing the corrosion-induced leak at Haldia Petrochemicals and preventing similar incidents in the future.
The diagram systematically identifies and categorizes potential causes of the leak by focusing on key areas. By mapping out these factors, a visual RCA tool like ProSolvr enables teams to pinpoint the primary contributors to corrosion, whether related to material selection, improper maintenance practices, inadequate corrosion protection measures, or environmental conditions within the plant. Once the potential causes are identified, the RCA process involves a detailed examination of each factor to determine the most significant underlying issues.
Who can learn from the Corrosion Induced Leak template?
Several groups can benefit from the insights gained through the Gen-AI-powered root cause analysis (RCA) of the corrosion-induced leak at Haldia Petrochemicals:
- Maintenance and Operations Teams: Learn about specific causes of corrosion in equipment and processes, allowing them to implement better inspection, maintenance, and operational practices.
- Engineering and Design Teams: Improve material selection, design of equipment, and overall process layouts to minimize corrosion risk in new projects and retrofits.
- Safety and Risk Management Teams: Gain valuable insights into potential hazards and the effectiveness of current safety protocols, aiding in the development of more robust risk management strategies.
- Plant Management and Leadership: Understand the importance of investing in preventive measures, proper training, and resources for effective corrosion management, ensuring long-term operational reliability.
- Quality Assurance Teams: Establish more stringent quality control processes in material procurement, inspection standards, and adherence to industry best practices.
- Environmental and Regulatory Bodies: Reinforce compliance with regulations and standards related to corrosion management, potentially influencing policy updates or new guidelines.
- Suppliers and Contractors: Improve the quality and suitability of products and services by understanding the specific needs of the plant through RCA insights.
- Other Petrochemical Companies: Use the findings as a case study to evaluate and improve their own corrosion management practices, reducing the risk of similar incidents industry wide.
Why use Corrosion Induced Leak template?
Implementing the findings from the fishbone diagram analysis will help prevent similar incidents in the future by addressing the root causes of corrosion. This could include updating materials used in high-risk areas, enhancing maintenance and inspection protocols, and improving training for staff on corrosion prevention techniques. Additionally, the insights gained can be applied across the plant, leading to a comprehensive review and strengthening of safety and operational practices.
By focusing on eliminating or controlling the root causes of corrosion, plants like Haldia Petrochemicals can significantly reduce the risk of future leaks, ensuring the continued safe and efficient operation of their facilities. Use ProSolvr by smartQED for efficient RCA at your petrochemical plants.
Draft and create a template for problem analysis in ProSolvr by smartQED.