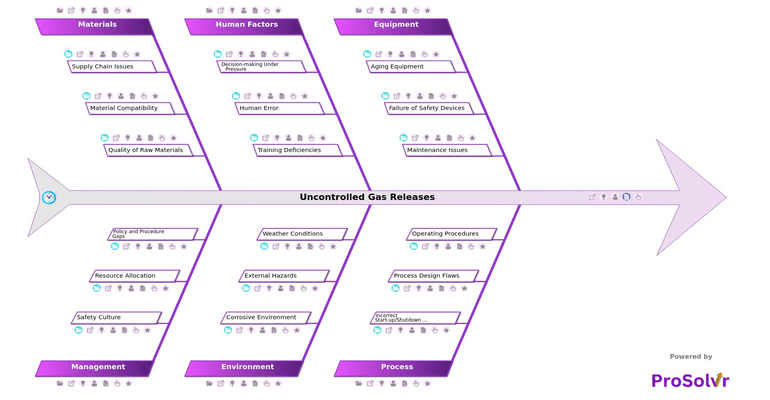
RCA of Uncontrolled Gas Releases
Uncontrolled gas releases in petrochemical plants are critical incidents involving the unintentional discharge of flammable or toxic gases into the environment. These events can be triggered by several factors, including equipment malfunctions, inadequate maintenance, operator errors, or external factors like corrosion or weather conditions. A structured fishbone analysis (Ishikawa diagram) is an invaluable tool for identifying and mitigating the root causes of these incidents.
The repercussions of uncontrolled gas releases are severe, with potential for catastrophic events like explosions, fires, and environmental contamination. Beyond the immediate physical dangers, these incidents pose significant operational and reputational risks, including regulatory fines and loss of public trust. Despite robust detection systems and strict adherence to safety protocols, these releases remain a persistent challenge, underscoring the necessity of root cause analysis to not only address the current issues but also implement sustainable preventative measures.
Applying Six Sigma principles within this RCA framework allows for a systematic approach to categorizing potential causes— whether stemming from mechanical, procedural, or human factors. By thoroughly mapping these relationships, plants can identify latent defects or gaps, such as improper calibration of safety valves or inadequate staff training. For instance, an equipment failure may highlight systemic issues in the preventive maintenance schedule, while operational errors could reveal deficiencies in the plant’s safety culture or communication processes.
Ultimately, leveraging RCA through tools like fishbone diagrams enables petrochemical plants to pinpoint precise failure modes, enhance safety protocols, and significantly reduce the likelihood of future gas releases. This proactive, data-driven approach fosters a more resilient operational environment.
Who can learn from the Uncontrolled Gas Releases template?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) of Uncontrolled Gas Releases provide valuable insights for various stakeholder
- Process Safety Engineers: To identify and mitigate potential hazards in petrochemical processes, ensuring safer plant operations.
- Maintenance Teams: To understand equipment-related risks, such as aging components and maintenance issues, and implement preventive measures.
- Operations Managers: To oversee the correct implementation of start-up/shutdown procedures and ensure adherence to operating standards.
- Training Coordinators: To design and conduct training programs that address human factors like decision-making under pressure and emergency procedures.
- Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) Professionals: To assess and manage the environmental factors and external hazards that could contribute to gas releases.
- Quality Assurance and Supply Chain Managers: To ensure the quality and compatibility of materials and manage supply chain risks that might impact plant safety.
Why use this template?
Using Gen-AI powered root cause analysis for the uncontrolled gas releases template is crucial for systematically identifying the underlying causes of such hazardous incidents. RCA helps organizations move beyond merely addressing the symptoms of a problem by uncovering the fundamental issues—whether related to equipment, processes, human factors, or management practices. By understanding these root causes, petrochemical plants can implement targeted corrective actions, enhance safety protocols, and prevent future occurrences of uncontrolled gas releases. This proactive approach not only safeguards human lives and the environment but also ensures regulatory compliance and operational efficiency.
Draft and create a template for problem analysis in ProSolvr by smartQED.