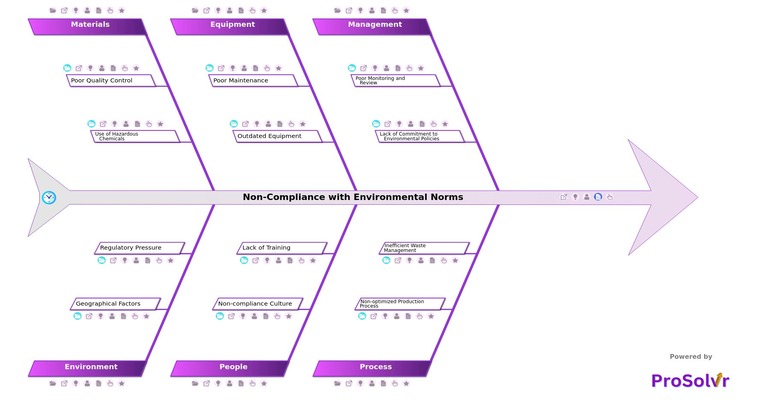
RCA of Non-Compliance with Environmental Norms
Between 2008 and 2010, Haldia Petrochemicals Limited (HPL) was scrutinized by the West Bengal Pollution Control Board (WBPCB) for non-compliance with environmental norms, particularly regarding air and water pollution. The main issues involved the discharge of untreated or inadequately treated effluents into nearby water bodies, posing significant risks to the Hooghly River and its aquatic ecosystem.
Additionally, the plant emitted pollutants at levels higher than permitted, raising health concerns among local residents. These violations highlighted shortcomings in the company's environmental management practices, including the operation of effluent treatment plants (ETPs) and air pollution control systems. These environmental breaches had severe consequences, affecting the local environment and the health and livelihoods of nearby communities. The WBPCB issued notices to HPL, demanding immediate corrective actions. The non-compliance also damaged the company's reputation, attracting increased scrutiny from environmental groups and the public. Despite HPL's efforts to address these issues, the recurrence of such incidents pointed to systemic problems within the company's environmental management and operational processes, necessitating a deeper investigation into the root causes.
A Root Cause Analysis (RCA) using a fishbone diagram can help address these issues by identifying the underlying causes of non-compliance rather than just treating the symptoms. By uncovering root causes, such as deficiencies in pollution control equipment maintenance, lapses in monitoring protocols, or insufficient employee training, HPL can implement targeted corrective actions. This approach not only resolves current issues but also prevents future occurrences, leading to more sustainable and compliant operations.
A systematic RCA can reveal the root causes of HPL's environmental non-compliance, allowing for targeted corrective actions. Addressing these root causes is essential for restoring compliance, safeguarding the environment, and maintaining HPL's reputation. The corrective, preventive, and investigative actions suggested will help HPL develop a more sustainable approach to operations, ensuring long-term environmental and regulatory compliance.
WWho can learn from the Non-Compliance with Environmental Norms template?
Several groups can benefit from the insights gained through the root cause analysis (RCA) of Non-Compliance with Environmental Norm:
- Environmental Compliance Officers: These professionals are responsible for ensuring that organizations adhere to environmental regulations. Learning from the RCA template can help them identify gaps in compliance and implement effective strategies to prevent future violations.
- Plant Operations Managers: Operations managers in industrial plants can use insights from the RCA to optimize production processes, improve equipment maintenance, and ensure that operations align with environmental standards.
- Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) Teams: HSE teams can use the RCA to enhance their safety protocols, conduct more effective environmental audits, and foster a culture of compliance within their organizations.
- Corporate Sustainability Officers: These officers focus on integrating sustainability into business operations. The RCA template can guide them in identifying areas where sustainability efforts may be lacking and how to strengthen environmental stewardship across the company.
- Regulatory Authorities and Inspectors: Government bodies and inspectors responsible for monitoring industrial compliance with environmental laws can learn from the RCA to better understand common non-compliance issues and refine their inspection and enforcement strategies.
- Environmental Advocacy Groups: NGOs and advocacy groups working to protect the environment can use the RCA findings to support their campaigns, push for stricter regulations, and engage with companies to improve their environmental practices.
Why use the Non-Compliance with Environmental Norms template?
The Gen-AI powered root cause analysis can be particularly useful for addressing non-compliance with environmental norms at Haldia Petrochemicals because it allows for a structured examination of all potential factors contributing to the issue. By categorizing causes with the Six Sigma principles, the fishbone diagram helps identify specific deficiencies, such as poor maintenance practices, inadequate training, or insufficient pollution control mechanisms. This visual and systematic approach ensures that all underlying causes are considered, enabling the development of targeted corrective actions to prevent future non-compliance and improve overall environmental performance.
Draft and create a template for problem analysis in ProSolvr by smartQED.