Malaysia Airlines Flight MH370's Disappearance
The disappearance of Malaysia Airlines Flight MH370 on March 8th, 2014, remains one of the most baffling and tragic mysteries in aviation history. ProSolvr for Root Cause Analysis can help unravel complex events and effectively investigate their causes.
MH370 was a scheduled passenger flight from Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, to Beijing, China. The airplane was a Boeing 777-200ER. There were 227 passengers and 12 crew members on board. The co-pilot made the last voice communication from the cockpit at 01:19 MYT. The plane was detected by military radar at 02:22 MYT over the Andaman Sea for the last time, hundreds of miles off course. The authorities never found the black boxes. Information about what happened in the final hours of MH370 is still missing, hampering the investigation and leaving many questions unanswered.
Authorities focused the search on the South China Sea. They later shifted to the Indian Ocean after military radar data indicated the plane had diverted westward. Investigators from the British company Inmarsat analyzed the satellite communications data. They believed the aircraft ended its flight in the southern Indian Ocean. They carried out a large-scale search in this remote area. The Australian Transport Safety Bureau (ATSB) led a thorough underwater search. It extended over an area of 120,000 sq. km. But they did not find any significant wreckage.
In conclusion, despite the extensive search efforts and analysis, the lack of conclusive evidence and the absence of the black boxes have made it incredibly challenging to determine the exact sequence of events leading to the disappearance of MH370. However, continued efforts in analyzing available data and applying systematic problem-solving approaches remain crucial in the ongoing quest for answers and closure for the families of the passengers and crew.
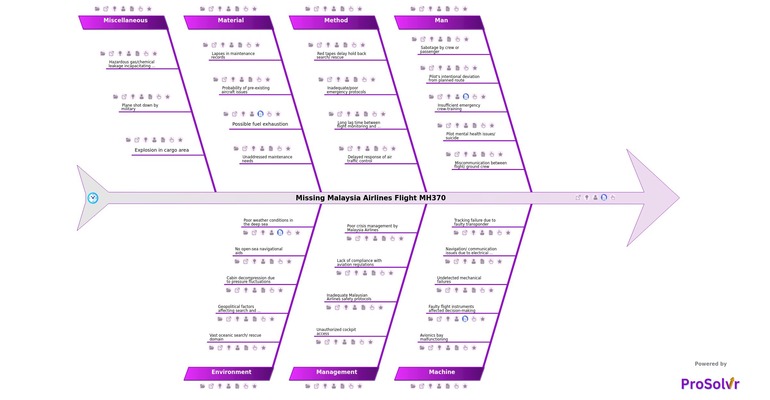
This fishbone diagram facilitates visual problem analysis. Within this Ishikawa diagram template lie crucial factors contributing to the disappearance of Malaysia Airlines Flight MH370.
Who should use the Missing Malaysia Airlines MH370 Flight template?
Why use the Missing Malaysia Airlines MH370 Flight template?
Create or customize your templates for problem analysis in ProSolvr by smartQED.
Curated from community experience and public sources: