RCA of Haneda Airport Runway Collision
On January 2, 2024, a collision shook Tokyo's Haneda Airport when a Japan Airlines (JAL) Airbus A350, arriving from New Chitose Airport near Sapporo, collided with a Japan Coast Guard Dash 8 aircraft. This incident, which occurred during the Coast Guard plane's preparation for departure to Niigata with earthquake relief supplies, resulted in a devastating fireball engulfing the JAL aircraft. Miraculously, all 379 passengers and crew on board the A350 were evacuated safely, but tragically, five out of the six crew members aboard the Coast Guard plane lost their lives, with the remaining member injured.
The evacuation process, despite challenges like a malfunctioning in-flight announcement system, was executed swiftly. Passengers used emergency slides, guided by crew instructions through megaphones, and completed the evacuation within 20 minutes. The fire was largely extinguished shortly after midnight.
This collision highlighted a critical miscommunication between air traffic control (ATC) and the pilots regarding runway usage. Investigations revealed that while the JAL plane had received clearance to land, the Coast Guard pilot misunderstood and proceeded with takeoff clearance. Such misunderstandings underscore the need for robust communication protocols and clear operational directives to prevent similar incidents in the future.
In conclusion, the Haneda Airport Runway Collision of 2024 serves as a stark reminder of the complexities and risks inherent in aviation operations. It emphasizes the urgent need for continual improvements in aviation safety protocols, including enhanced training, improved communication, and rigorous adherence to operational standards. By conducting a thorough root cause analysis and implementing effective corrective and preventive actions (CAPA), the aviation industry can mitigate risks and ensure safer skies for passengers and crew worldwide.
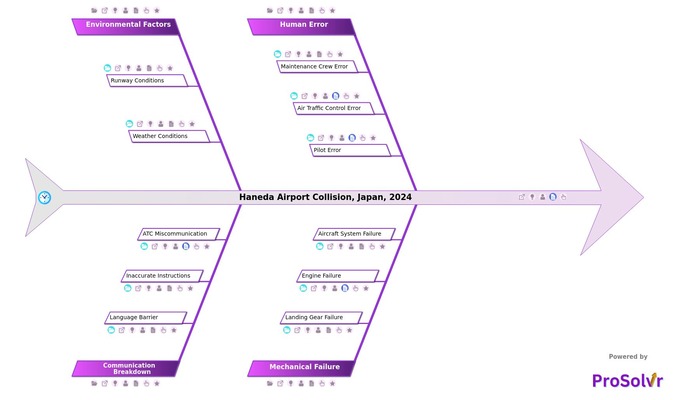
The Haneda Airport Collision in Japan, 2024, involved multiple factors such as human error (maintenance crew, air traffic control, and pilot errors), mechanical failures (landing gear, engine, and aircraft system issues), environmental factors (runway conditions and weather), and communication breakdowns (language barriers and ATC miscommunication). These combined issues led to the unfortunate incident.
Who Can Learn from the Haneda Airport Runway Collision?
- Airlines: Strengthen training programs focused on emergency response and fatigue management to promote operational excellence and reliability during crises.
- Pilots: Reinforce adherence to standard procedures and verification of clearance instructions to enhance safety and prevent miscommunications.
- Air Traffic Control (ATC) Personnel: Improve communication protocols to ensure clarity and prevent misunderstandings during critical operations.
- Enhanced Situational Awareness: Implement advanced training and technology adoption to enhance situational awareness and mitigate similar incidents.
- Airport Authorities: Review and update runway management systems to prevent simultaneous aircraft movements and ensure compliance with international safety standards.
- Regulatory Bodies: Utilize insights from this incident to update aviation safety policies, conduct regular audits, and enforce compliance to foster continuous improvement and enhance overall safety measures in aviation.
Why use the Haneda Airport Runway Collision template?
The Haneda Airport Runway Collision underscores the imperative for continual improvements in aviation safety, operational excellence, and quality and reliability. By implementing robust CAPA strategies derived from comprehensive root cause analysis, the aviation industry can mitigate risks and enhance safety measures effectively. Applications like ProSolvr facilitate efficient problem-solving and contribute to safer skies, ensuring incidents like the Haneda collision serve as lessons for continuous improvement.
Create or customize your templates for problem analysis in ProSolvr by smartQED.
Curated from community experience and public sources: