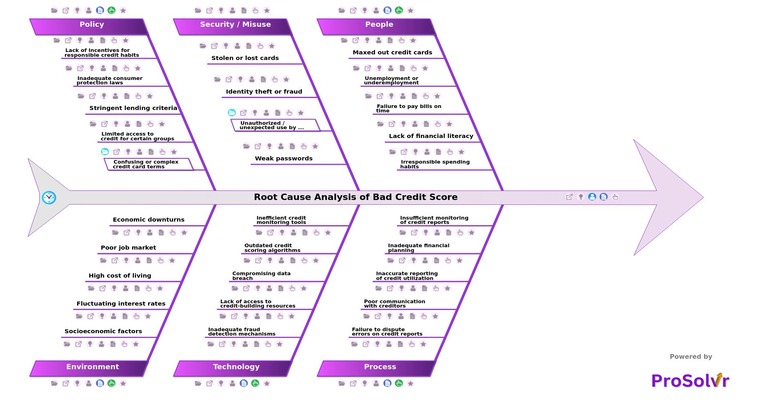
Root Cause Analysis of Bad Credit Score
Root cause analysis (RCA) is a systematic process used to identify the underlying causes of problems or issues. When it comes to a bad credit score, RCA helps in pinpointing the exact reasons why someone's credit score is not up to the mark. This analysis is crucial for implementing effective solutions that can lead to credit improvement.
In the context of Six Sigma methodologies, which emphasize data-driven decision-making and process improvement, RCA plays a pivotal role. By applying Six Sigma principles to credit analysis, we can identify the critical factors contributing to poor credit scores with precision. This data-driven approach ensures that the solutions implemented are not just quick fixes but are sustainable and impactful in the long run.
Common root causes of bad credit scores often include late payments, high credit utilization, errors in credit reports, and lack of credit history. These factors can significantly impact an individual's creditworthiness and make it challenging to secure loans or favorable interest rates. Through a thorough RCA, these issues can be identified and addressed systematically, paving the way for credit score improvement.
ProSolvr offers a state-of-the-art AI-powered visual root cause analysis tool designed to facilitate effective problem-solving for bad credit scores. Our tool delves deep into credit data, revealing hidden patterns and insights that traditional methods might overlook. By utilizing ProSolvr's innovative solutions, users can identify the root causes of their credit challenges with precision. This empowers them to make informed decisions and take proactive steps towards improving their financial situation and achieving long-term stability.
Poor credit scores, as depicted in the fishbone diagram, stem from issues such as late payments, high credit utilization, and financial mismanagement. To improve your credit score, ensure timely payments, manage credit usage responsibly, and enhance financial planning. Recognizing and tackling these root causes can pave the way for credit improvement and financial stability.
Who should use the Bad Credit Score template?
The Bad Credit Score fishbone template is designed for individuals, financial advisors, credit counselors, and anyone interested in understanding and improving their credit situation. Whether you're facing challenges with your credit score or seeking ways to help others manage their credit more effectively, this template can serve as a valuable tool. It offers insights into common factors contributing to bad credit scores and provides actionable steps to address them, making it suitable for a wide range of users looking to enhance their financial health.
Why use the Bad Credit Score template?
- Insightful Analysis: The template provides a structured framework to identify the root causes of bad credit scores, helping users understand the factors affecting their financial health.
- Actionable Solutions: With clear categories and detailed explanations, the template offers actionable steps to address each root cause, empowering users to take proactive measures to improve their credit situation.
- Educational Tool: The template serves as an educational resource, offering valuable information on credit management, financial literacy, and responsible borrowing practices.
- Efficiency: By utilizing a well-organized template, users can save time and effort in conducting their own research and analysis, as the key information is already compiled in a user-friendly format.
- Customizable: The template can be adapted to fit individual needs and preferences, allowing users to focus on specific areas of concern or interest related to bad credit scores.
Overall, the Bad Credit Score template serves as a comprehensive guide for understanding, analyzing, and addressing credit challenges, making it a valuable resource for anyone looking to improve their financial well-being.
Draft and create a template for problem analysis in ProSolvr by smartQED.
Curated from community experience and public sources: